How do you increase the amount of acetylcholine in your brain? There might not be such thing as pure acetylcholine supplements, but there are many well-researched supplements that you can take to raise levels of this neurotransmitter.
Acetylcholine supplements are the foundation of many nootropic stacks, and it plays a super important role in the formation of memory. The function of acetylcholine also regulates everything from salvation to mood, cognition, and digestion.
Why should you care about taking acetylcholine supplement? Take some time and read this research.
What Is Acetylcholine and What Does Acetylcholine Do
Acetylcholine is an organic cation that acts as a neurotransmitter in the choline synapses in the central and peripheral nervous systems.
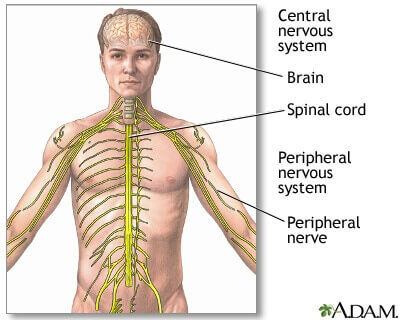
It is one of the neurotransmitters in the autonomic nervous system that has an important role in the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts and is the only neurotransmitter that is used in the motor part of the somatic nervous system.
Acetylcholine is responsible for the volitional control of the body and is part of the peripheral nervous system. Acetylcholine and acetylcholine supplement is important for both the central and the peripheral nervous system.
In the peripheral nervous system, it has a role in the activation of the muscles due to the high concentration of acetylcholine receptors in the skeletal muscle fibers.
Acetylcholine improves not only the contractions of the skeletal muscles but also the cardiac muscles. In the central nervous system, acetylcholine forms the neurotransmitter system, which is called cholinergic and has an anti-excitatory effect.
Acetylcholine function and its participation in the central nervous system are associated with waking up from sleep, sleep quality, maintaining focus, memory, brain activity as a whole, decision-making, and movement control.
Bottom Line:
Acetylcholine and acetylcholine supplement is important for both the central and the peripheral nervous system.
Acetylcholine function and its participation in the central nervous system are associated with waking up from sleep, sleep quality, maintaining focus, memory, brain activity as a whole, decision-making, and movement control.
My Top 4 Natural Brain Enhancing Supplements
1) Doctor's Best Natural Brain Enhancers PS & GPC
Product Overview:
- Science-Based Nutrition
- Dietary Supplement
- Promotes Memory & Attention
- Vegan
- Non-GMO and Gluten-Free
Doctor's Best Natural Brain Enhancers PS & GPC Benefits
GPC (GlyceroPhosphoCholine) and PS (PhosphatidylSerine) have several proven benefits to various cognitive functions. These phospholipid nutrients work very well together, due to their different mechanisms of action.
GPC can be found in its highest concentrations inside the cells, while PS helps to build the cell membranes that supply the brain with electricity and vital energy. The benefits of GPC and PS have been evidenced in multiple random, double-blind trials. These nutrients are proven to be effective in humans of all ages:
- Improve various cognitive functions such as attention, memory and learning abilities;
- Helps the brain to cope with stress;
- Enable growth factor action for the renewal of the brain circuits.
How to Take Doctor's Best Natural Brain Enhancers PS & GPC
- Take 2 capsules daily between meals, not later than 4 pm.
2) Now Foods Brain Elevate

Product Overview:
- Cognitive Health;
- With Memorzine Huperzine A, Alpha-GPC & Phosphatidyl Serine;
- Supports Memory, Learning, and Alertness;
- Vegetarian/Vegan;
- GMP Quality Assured;
- Gluten-Free.
Now Foods Brain Elevate Benefits
Now Foods Brain Elevate is a supplement that promotes mental alertness and learning, thanks to its ability to stimulate the production and the activity of Acetylcholine (ACh). ACh is one of the most important neurotransmitters, with a major role in regulating cognitive and neural function.
ACh production tends to decrease as we age. The Alpha-GPC combination in RememBrain as the ability to boost ACh production with Memorzine Huperzine A, thus maintaining ACh levels in the brain.
This supplement also includes Phosphatidyl Serine, a compound that plays an important role in supporting the health of membranes and the efficiency of nerve cell signaling.
How to Take Now Foods Brain Elevate
- Take 2 capsules 1 to 2 times daily.
3) Jarrow Formulas Neuro Optimizer
Product Overview:
- Supports Brain Health and Function
- Gluten-Free
Jarrow Formulas Neuro Optimizer Benefits
Jarrow Formulas Neuro Optimizer is pure food for the brain, thanks to its unique combination of nutrients that accelerate brain metabolism and offer effective antioxidant protection in a safe and natural way.
Citicoline (CDP-Choline) promotes the synthesis of phosphatidylcholine, one of the main compounds in the gray matter of our brains. Citicoline acts as a catalyst in the synthesis of acetylcholine, being, therefore, a brain metabolism promoter and an effective phospholipid generator.
PA (Phosphatidylserine) helps to promote neural communication while being also very effective in improving the brain's response to stress. The antioxidant substances are actively fighting oxidative processes in the brain, therefore protecting the neurons against oxidation.
Acetyl L-Carnitine and L-Glutamine are also regulators of energy utilization. Taurine is important in intracellular osmoregulation, which means it helps to maintain the healthy concentrations of ions inside the cells.
How to Take Jarrow Formulas Neuro Optimizer
- Take 4 capsules per day with juice or water between meals.
4) Life Extension Cognitex Basics
Product Overview:
- Supports Healthy Brain Cell Function
Life Extension Cognitex Basics Benefits
Life Extension Cognitex formula dates back from 1982 when Life Extension developed it with the purpose of providing support for the brain of aging people.
Today's Cognitex Basics is a less expensive yet very powerful product, featuring two important compounds that can't be supplied through adequate nutrition:
L-alpha glyceryl phosphorylcholine (Alpha-GPC) is naturally occurring in the membrane of most cells in the human body. Cognitex provides this compound as an essential building block for acetylcholine production in the brain.
Our brain needs acetylcholine for muscle control, sleep, and cognition processes. Alpha-GPC helps to recycle phospholipids, so the more you have, the better your phospholipid synthesis. The result is a more efficient signal transduction by the central nervous system.
Phosphatidylserine (PS) is another essential building block in the human brain. It can be found in most brain tissues.
Nonetheless, aging can cause a decrease in the PS content of the tissues, therefore leading to cognitive decline. Phosphatidylserine plays a very important role in the healthy cellular division of nerves and in supporting the memory functions.
How to Take Life Extension Cognitex Basics
- Take two (2) softgels in the morning with or without food.
What Are the Neurotransmitters and How to Increase the Neurotransmitters in the Brain
The nervous system is an integral part of the body of any animal, including in humans. Neurotransmitters' main function is to coordinate the actions and to transmit signals between different parts of the body.
At a cellular level, the nervous system functions through the nerve cells or neurons that send signals in the form of electrochemical waves through the nerve fibers (axons) that cause synapses to release chemicals, called neurotransmitters.
The neurotransmitter is a chemical that acts as a "messenger," sending, stimulating and regulating signals between neurons and other cells in the body.
It is released from the synapses, reaching the receptors of the neurons or the other cells; it binds to the receptors in the chain, and at the end of the process, it is absorbed by the neurons.
So, is acetylcholine a neurotransmitter?
Yes, acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter, and the neurotransmitters are the ones responsible for the transmission of information in the human body.
Types of Neurotransmitters:
Depending on their structure, the neurotransmitters are divided into:
1) Amino Acids
- Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)
- Glycine
- Glutamate
- Aspartate
2) Biogenic amines or monoamines (aromatic amino acids)
- Dopamine
- Octopamine
- Tyramine
- Norepinephrine
- Epinephrine
- Norepinephrine
- Melatonin
- Histamine
- Serotonin
3) Peptides
- Somatostatin
- Substance P
- Endorphins
4) Independent Neurotransmitters
- Acetylcholine
- Nitric oxide
- Adenosine (and others)
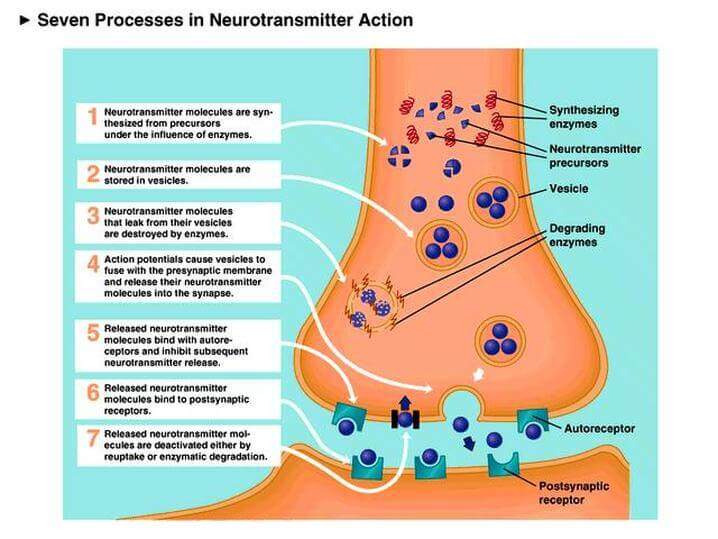
Original source here.
The neurotransmitters are divided into two main types, depending on their effect on the nervous system. They can be excitatory, causing an action in nerve cells or being inhibitory, causing the opposite action - inactivity of the nerve cells.
So is acetylcholine excitatory or inhibitory?
In fact, the direct effect of the neurotransmitters is limited to the activation of one or more of the receptors, as the excitatory or inhibitory action depends on the nature of the receptor itself.
Some receptors have a totally excitatory action (glutamate), while others have an inhibitory effect (GABA). Third ones, like the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, are typical for causing both effects - excitatory and inhibitory.
Bottom Line:
Depending on neurotransmitters' effect on the nervous system, they can be excitatory, causing an action in nerve cells or being inhibitory, causing the opposite action - inactivity of the nerve cells. The neurotransmitter acetylcholine is typical for causing both effects - excitatory and inhibitory.
Precursors of the Neurotransmitters
A great part of the neurotransmitters cannot be found in food and therefore have no direct natural source. For this purpose, the neurotransmitters are synthesized by their precursors, whose sources are foods, herbs, or acetylcholine supplement.
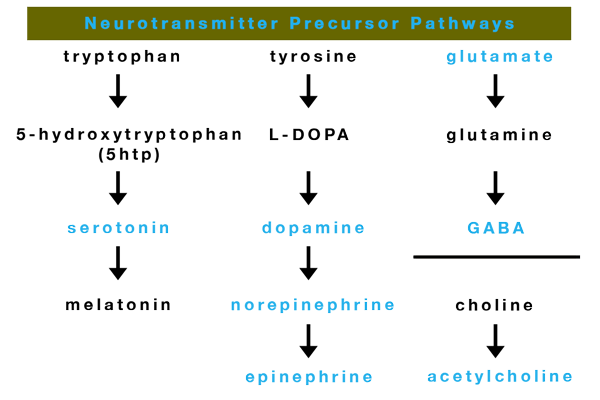
Original source here.
- One of the strongest precursors of the neurotransmitters is L-Dopa, a chemical that can be found in some natural sources like animals and plants. Animals, including humans, synthesize L-Dopa from the amino acid L-tyrosine. L-Dopa is found in large quantities in some herbs as velvet bean (Mucuna pruriens) and broad bean (Vicia faba). L-Dopa is a precursor of the powerful neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine.
- The amino acids phenylalanine and tyrosine also possess properties of precursors of dopamine, octopamine, tyramine and norepinephrine, epinephrine, but the metabolic processes require the involvement of some important coenzymes, such as vitamin B-6 and other mediators.
- Proven precursors of the serotonin neurotransmitter are the amino acid L-tryptophan, for the conversion of which vitamin C is needed. Another powerful precursor of serotonin is the amino acid 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP), which is extracted from the plant Griffonia simplicifolia.
- In vivo studies have shown that the amino acid glutamine successfully increases the levels of GABA, but due to some conflicting results on the effectiveness of glutamine when taken orally, it is difficult to prove the potential benefits of glutamine as a precursor.
- Acetyl-L-Carnitine, Huperzine A, and Alpha-Glycerylphosphorylcholine (Alpha-GPC) are proven precursors of acetylcholine neurotransmitter, while the clinical results for dimethylaminoethanol (DMAE) are still controversial.
The Structures 0f Neurotransmitters
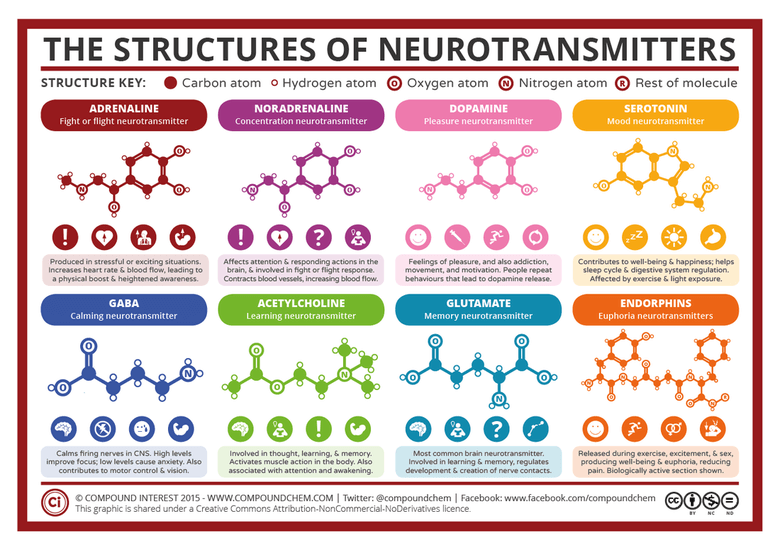
Original source compoundchem.com. Click here for a larger view.
Potential and Proven Benefits with the Uptake of Neurotransmitters and Acetylcholine Supplement Benefits
- GABA shows potential benefits in the promotion of peace and the regulation of aggression in people. Other benefits are associated with the strengthening of the immune system in conditions of stress, reducing the time for falling asleep, and the increasing of the levels of the growth hormone at rest or after exercises;
- Glycine successfully enhances the potency of the n-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptors. Scientific researches on humans demonstrate the benefits of 3000 mg of glycine before bedtime for the improvement of sleep and sleep quality. There are claims for potential benefits of reducing the cortisol levels with an intake of over 10 grams per day;
- It was found that L-Dopa successfully crosses the blood-brain barrier, which is impossible for dopamine; that is why L-Dopa successfully increases the levels of dopamine in the brain. Also, L-Dopa increases the levels of the growth hormone in the plasma for 2 hours after administration and has been used successfully used in the therapy of Parkinson's disease. One of the richest natural sources of L-DOPA, the velvet bean herb, shows effects of an antidepressant, as tests have suggested that it leads to better results in the treatment of Parkinson's disease in comparison with the administration of pure L-Dopa;
- Research on L-tryptophan leads to controversial results. Different conclusions are related to the efficiency of tryptophan as an aid to sleep. Some of them suggest that it is ineffective in individuals without sleep problems. Tryptophan shows promising results with low serotonin levels, as an antidepressant and as a strengthening agent for other antidepressants. In the US, the use of the pure form of L-tryptophan has been prohibited for a long time from the FDA, but after 2001 the control over the substance has been weakened. In Europe and the EU, there are no such restrictions, or there is a complete lack of regulation in the separate countries;
- 5-HTP shows positive results in states of depression, nervousness, high appetite, insomnia. In vivo studies have shown that the administration of the substance has successfully increased the serotonin levels in the brain, also the growth hormone in the plasma. It also has been used successfully for the treatment of diseases such as myofibrillar syndrome and Friedrich's ataxia. The antidepressant properties are expressed most strongly when combined with L-tryptophan and therefore scientists cannot say that 5-HTP standalone has pronounced antidepressant properties;
- L-phenylalanine is a biological precursor of L-tyrosine. When phenylalanine is taken in higher doses, it has a positive influence on serotonin levels. Admission as a dietary supplement has supposed benefits associated with some antidepressant actions, improved sleep, reduced appetite, and analgesic effect;
- Studies of L-tyrosine have to lead to the conclusion that the amino acid is an effective precursor of the neurotransmitters dopamine, epinephrine, and norepinephrine. The effects of L-tyrosine on the mood occur only under stress, cold, fatigue, and lack of sleep. L-tyrosine positively affects the concentration, mental attitude, reduces the stress hormones, the weight loss due to stress, mental and physical exertion in severe conditions. L-tyrosine does not have a positive influence on the mood, but higher doses may decrease the levels of dopamine. L-tyrosine reduces the absorption of L-Dopa;
Where Can We Find Supplements to Support Our Neurotransmitters
Some neurotransmitters as GABA and glycine can be easily found among the brands of the larger manufacturers of health supplements. They typically come in the form of capsules, but some brands are also available as a powder.
More common are the precursors of the neurotransmitters, they are also present in the ranges of supplements by most health supplements manufacturers. Popular precursors on our market are acetyl-L-carnitine, Alpha-GPC, 5-HTP, Mucuna pruriens, L-tyrosine, L-phenylalanine, and others.
The neurotransmitters and their precursors are not new to complex formulas. They are often part of the complexes for sleep or nocturnal stimulation of the growth hormone, for studying and brain stress, for relaxation, as some of the excitatory ones are used in pre-workout sports formulas.
Where Is Acetylcholine Found and How Does Acetylcholine Work
The sources of acetylcholine are a separate category of nootropics (neurostimulators) that include different groups of substances. Let's talk about each source of choline and acetylcholine groups, separately below.
1) Choline and Acetylcholine Precursors
First, there are the acetylcholine precursors. They are some of the best supplements to increase acetylcholine.
Choline and acetylcholine precursors are compounds which, after several enzymatic reactions, are converted into acetylcholine, as some of them contain choline in their formulas.
Some of the most popular precursors are:
- Choline bitartrate
- DMAE (dimethylaminoethanol)
- Alpha-GPC (L-alpha Glycerylphosphorylcholine)
- CDP-Choline (Cytidine 5-diphosphocholine)
2) Co-Factors in the Formation of Acetylcholine
Secondly, there are substances that act as co-factors in the formation of acetylcholine. The co-factors are assisting molecules that accelerate or stimulate the biochemical transformations in the body, in this case, the formation of acetylcholine.
Popular co-factors of acetylcholine are:
- Acetyl-L-Carnitine
- Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic acid)
3) Acetylcholinesterase Antagonists
The third group of substances that are involved in the synthesis of acetylcholine is inhibitors of the acetylcholinesterase enzyme, which is involved in the breakdown of acetylcholine.
The levels of the acetylcholine neurotransmitter are increased with the inhibition of the enzyme. Such acetylcholine inhibitors are:
- Huperzine-A (from Huperzia Serrata)
- Rosemary
- Cannabis
- Galantamine
4) Acetylcholine Agonists
The fourth group of supplements includes many of the most popular nootropics. They are also named as acetylcholine agonists or cholinergic supplements.
- Piracetam
- Aniracetam
- Pramiracetam
- Oxiracetam
- Noopept
Their path of action is to stimulate your acetylcholine receptors to release more of the stored neurotransmitter.
Having higher levels of acetylcholine makes it easier for your brain to form new connections between neurons, to store new memories, and to recall old memories.
A higher concentration of acetylcholine in the cerebral cortex has also been shown to increase attention span, focus, neuroplasticity, and communication between the left and right hemispheres of your brain.
Bottom line:
Because of their unique mechanism of action, acetylcholine agonists are the most effective at increasing levels of this neurotransmitter’s activity in the brain.
5) Acetylcholine Antagonists
Another group of substances that would increase the levels of acetylcholine are its antagonists. The antagonists bind to the receptors of the cells and obtain the same response. They often mimic the action of acetylcholine. A popular antagonist is:
- Nicotine
What Is Acetylcholinesterase
Acetylcholinesterase, also known as AChE or acetylhydrolase, is an enzyme that breaks down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine at the synaptic cleft (the space between two nerve cells) so the next nerve impulse can be transmitted across the synaptic gap.
Acetylcholinesterase is the primary cholinesterase in the body. It is an important enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of acetylcholine and of some other choline esters that function as neurotransmitters.
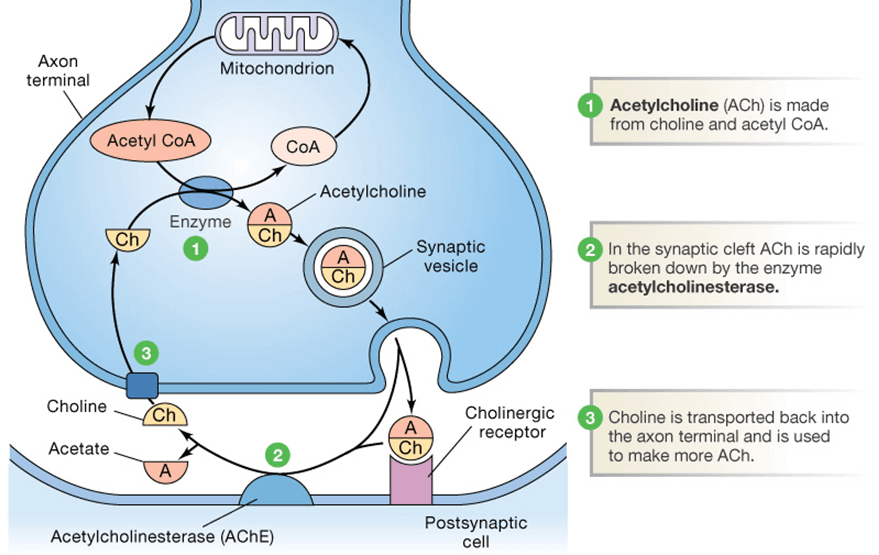
Found at mainly neuromuscular junctions and in chemical synapses of the cholinergic type, Acetylcholinesterase’s activity serves to terminate synaptic transmission. It is the primary target of inhibition by organophosphorus compounds such as nerve agents and pesticides.
Acetylcholine Synthesis, Storage and Release
Acetylcholine is synthesized from its two immediate precursors, choline and acetyl coenzyme A by the enzyme choline acetyltransferase. Coenzyme A is synthesized in mitochondria and accesses choline acetyltransferase following transport across the mitochondrial membrane into the cytoplasm.
In addition to its synthesis in the liver, choline engaged in acetylcholine production is derived from dietary sources. Ther carrier system in capillary endothelial cells is responsible for the transport of choline
into the brain.
Hydrolysis of choline-containing phospholipids may also liberate choline that is used in acetylcholine synthesis. It appears that the rate of acetylcholine synthesis is dependent on precursor availability.
Enzyme activity is also regulated by-product inhibition; by binding at an allosteric site on choline acetyltransferase, acetylcholine inhibits its activity. A specific low-affinity acetylcholine transporter is responsible for the uptake of the transmitter from the cytoplasm into vesicles.
Once packaged in vesicles, acetylcholine is subject to stimulus-induced released by exocytosis. Neuronal acetylcholinesterase very rapidly inactivates the majority of acetylcholine released in the brain.
In the periphery, acetylcholinesterase is present in muscle that receives cholinergic innervation. Choline, which is liberated from acetylcholine by acetylcholinesterase, is taken back up into cholinergic terminals by a high-affinity transporter and reused in transmitter synthesis.
What is the Acetylcholine Effect on Human Body
In response to input from the nervous system, muscle, striated, or skeletal muscle cells usually contract. It is a structure with the name motor end plate where a motor neuron contracts.
The membrane of the muscle cells contains acetylcholine-sensitive nicotinic receptors. The receptor molecules are protein-based and are in large concentrations where the release of acetylcholine happens.
The nicotinic receptor is a sodium channel that is ligand-gated, which means that once acetylcholine is released, the ligand will bind to a receptor, which subsequently transforms its shape to allow the entry of sodium into the muscle cell.
1) The Effect of Acetylcholine on the Muscle Membrane
The entry of sodium results in depolarization of the muscle cell in the motor endplate's vicinity. Depolarization refers to a reduction in the difference in charge between the exterior and interior of the muscle.
In response to the depolarization, activation of a different type of sodium channel happens that allows the entry of more sodium, spreading the wave of excitation throughout the muscle cell.
Consequently, calcium ions are released from the storage sites within the cells of the muscle. Calcium ions trigger a series of biochemical events that involve myosin, tropomyosin, and troponin, which causes contraction of the muscle.
2) The Effect of Acetylcholine on Smooth Muscle
The muscarinic receptor is another type of receptor found in the smooth muscle that is also activated by acetylcholine. Once the receptor binds acetylcholine, it leads to a release of calcium ions from the internal stores.
The reaction of acetylcholine with the muscarinic receptors causes opening of the channels just as with nicotinic receptors and ions flow, thereby depolarizing the muscle cell. Depolarization results in contraction of the muscle just as in a skeletal muscle.
3) The Effect of Acetylcholine on Cardiac Muscle
The cardiac muscle also has muscarinic receptors, just like a smooth muscle. However, the effect of acetylcholine on the cardiac muscle differs from its effects on smooth or skeletal muscle.
The activation of the muscarinic receptors by acetylcholine in the heart results in the channels in the muscle membrane allowing potassium to pass. This results in slowing down of the contraction of the heart muscle and makes the heartbeat with less force.
Acetylcholine and Alzheimer's Disease
The progressive damage to the cells of the brain and the ensuing loss of neurotransmitters, which are the chemicals that the cells produce is what causes Alzheimer's.
Acetylcholine is one of the neurotransmitters, and once its levels plummet, it results in problems such as difficulty with attention and memory retention, which is common for people suffering from Alzheimer's.
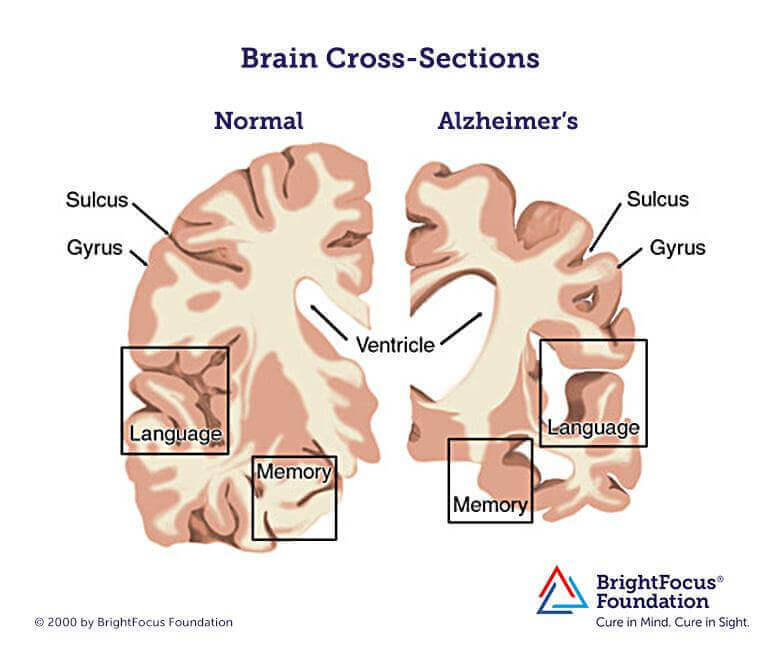
Original source here.
1) The Relationship Between Cholinergic Neurons and Alzheimer's
Alzheimer's disease mostly affects the cholinergic neurons situated in the area referred to as the nucleus basalis of Meynert (NbM), which is located in a structure known as the basal forebrain.
The neurons connected to other parts of the brain, known as the amygdala and cortex, which are responsible for the regulation of emotions, attention, memory, and learning, are housed in the NbM.
2) What Causes the Loss of Cholinergic Neurons
Plaques containing the fibrillar substance beta-amyloid are usually seen in Alzheimer's brains, but no direct connection exists between the location and number of plaques and the loss of cholinergic neurons.
Instead, the loss is more closely associated with a soluble form of beta-amyloid, which disrupts acetylcholine's production and release, as well as interfering with the actions of nerve growth factor, which is a chemical involved in maintaining the function and structure of cholinergic neurons.
Other indications are that damage could be as a result of the immune system reacting to fibrillary beta amyloid's initial production before the formation of the plaque, which involves releasing harmful chemicals.
The Solution
The release of the enzyme acetylcholinesterase is inhibited by acetylcholinesterase. Acetylcholinesterase is responsible for breaking down acetylcholine once released. However, acetylcholinesterase inhibitors don't prevent the destruction of the cholinergic cells.
This means that even though they can boost the performance of a person suffering from Alzheimer's temporarily, their main advantage is that acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are capable of slowing down the progressions of decline be ensuring that acetylcholine levels stay as high as possible in spite of cell destruction and damage.
Picking the Right Acetylcholine Supplement
I use nootropics 4-5 times per year. Each period lasts around 1 month. The last nootropic stack I used is the below mentioned: "Acetylcholine supplement stack for beginners."
Check out both acetylcholine supplement stacks below. I have included some details about the stack, like the acetylcholine supplement dosage.
Below are the best acetylcholine supplements according to my experience. The two stacks are designed to increase the acetylcholine in the brain
Acetylcholine Supplements Stack Done the Right Way
I will present to you two nootropic stacks, as they are one of the best cognitive enhancers I have ever used. The first one is appropriate for those who would like to try a nootropic stack for the first time. To see how it acts and if it is appropriate for them.
The second one is more advanced. thus it is designed to provide much more benefits on memory and cognition.
1) Acetylcholine Supplements Stack for Beginners
- 1000 mg - Alpha GPC
- 10 mg - Noopept
- 1500 mg - Fish Oil (EPA + DHA)
- 500 mg - Acetyl-L-Carnitine
- 300 mg - Bacopa Monnieri
2) Advanced Acetylcholine Supplements Stack
- 100 mg - Phenylpiracetam
- 10 mg - Noopept
- 300 mg - Bacopa Monnieri
- 1000 mg - Alpha GPC
- 200 mg - Caffeine
- 50 mcg - Huperzine A
- 30 mg - Vinpocetine
- 350 mg - DMAE
- 500 mg - Acetyl-L-Carnitine
- 500 mg - L-Tyrosine
Natural Supplements for Memory and Cognition
We all know that the intellectual activity is just as exhausting as the physical one, and sometimes the loading of the brain and central nervous system can be a double-edged sword, which can lead to even more fatigue and more difficult recovery from the adverse effects afterward.
Memory and concentration are the two main assets for achieving high scores on exams. Occupations, which overtax the brain activity, as well as educational classes, establish additional requirements for the recovery of the nervous system.
These requirements can not be met by the normal diet or the amount of sleep in our everyday life. The restoration of the central nervous system is negatively affected by factors, such as frequent exposure to monitors, wireless networks, and cellular phones.
In the rest of this article, we will look through the consumer’s options on the best memory supplements and the best brain supplements that maintain the body’s cognitive activity.
To make the intake of food supplements as effective as possible, we will differentiate two main approaches, namely - the momentary stimulation of the brain activity and concentration and the long-term support of the nervous system.
Broadly speaking, young people must have three goals for themselves to achieve the top condition of their brains - to improve their alertness, memory, and to protect themselves from stress.
How to Stimulate the Brain When We are Expecting Heavy Mental Work
1) Caffeine + L-Theanine
Caffeine is a well-known nervous system stimulator and cognate enhancer that improves the momentary tone, concentration, and brain activity. The disadvantage of caffeine is its ability to exhaust the central nervous system.
An interesting fact - studies show that the combining of caffeine with the L-theanine amino acid indicates more stable and reliable results than the intake of either of the two substances separately.
The concomitant intake of caffeine and L-theanine improves the concentration, mood, and duration of mental work dramatically. The key combination lies in L-theanine’s ability to suppress the overstimulating and exhausting properties of caffeine while retaining its positive qualities.
Dosage:
- The recommended intake is 200 mg of caffeine and 200 mg of L-theanine, 30-60 minutes before mental strain. Take them on an empty stomach for better results.
2) Cholinergic Supplements
The cholinergic supplements are a class of substances that increase the levels of acetylcholine in the brain. Acetylcholine is an important neurotransmitter that plays a key role in the overall cognitive activity, concentration, stamina, and nervous system recovery.
The most popular cholinergics drugs are CDP-Choline, Alpha-GPC, Huperzine-A, and Acetyl-L-Carnitine. The cholinergic supplements are beneficial in short and the long-term. In the short term, these cholinergic drugs stimulate the momentary tone and concentration.
This is the reason why they are widely used in pre-workout products, also knows as nitrogen boosters. In the long term, they support the brain functions and the central nervous system recovery and functioning.
Dosage:
- Alpha-GPC - 300-600 mg daily;
- CDP-Choline - 250-500 mg daily;
- Acetyl L- Carnitine - 2,000 mg per day;
- Huperzine A - 50-200 mcg daily.
Long-Term Support of the Brain Activity
1) Vinpocetine
Vinpocetine is a natural substance, contained in the lesser periwinkle plant/Vinca minor. Vinpocetine shows promising results in human studies as brain enhancing supplements.
A dose of 40 mg, 1 hour before the mental activity, drastically improves memory in the Sternberg test. The positive effect of vinpocetine can be seen in the mood, focus, and reaction time improvement. The substance has also demonstrated promising results in the prevention of Alzheimer's disease.
The possible mechanism of working of vinpocetine is associated with the improvement of the blood supply to the brain, as well as the protection of the brain tissues from damage by free radicals.
Dosage:
- Take 20-40 mg vinpocetine daily, preferably on an empty stomach, 1-2 hours before mental strain.
2) Blueberry Extract
Blueberries are ranked as having one of the highest antioxidant capacities among foods. They are a rich source of the important substances anthocyanins and pterostilbenes. It is these two substances that can affect brain activity and protect the brain from damage.
Blueberries stimulate the activity of the growth factor, known as a nerve growth factor (NGF). When neurons grow, they get connected with other neurons. NGF stimulates their growth and improves communication between the neurons.
At this stage, human studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of blueberries only in adults, but many animal studies indicate that blueberries have a positive impact on brain activity as a whole, regardless of the age factor.
Dosage:
- It is believed that 500-1000 mg of anthocyanins per day is enough to support brain function.
3) Fish Oil (Omega-3)
Fish oil is an important and potent source of the two major omega-3 fatty acids - EPA and DHA. DHA is an important element for proper brain functioning. Therefore, the greater part of its content in the body is concentrated in the brain.
DHA is a major building block in the brain, and it directly affects the numerous brain processes and functions of the nervous system.
The serious deficiency of DHA is associated with some cognitive and mental health problems - memory loss, depression, mood, dementia, Alzheimer's syndrome, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
It has been found that high doses of DHA directly improve the mood, memory, nervous system functioning, and people’s condition in specific cognitive disorders.
Dosage:
- The recommended intake of EPA+DHA is 1000 - 2000 mg.
4) Bacopa Monnieri
Bacopa is a marshy plant, and its properties to help stimulate cognitive activity have been known to the traditional Ayurvedic medicine. Although Bacopa Monnieri is most effective in older adults, a positive impact has been reported in all age groups.
Scientific researchers have established that Bacopa improves the working memory dramatically, as there may be potential properties for also improving the attention, speech, and reactions.
The working memory is one’s ability to focus on a topic to understand and memorize. Bacopa is not a supplement with an immediate effect. Studies show that the benefits of the herb occur after a month of usage.
Dosage:
- The main active ingredient in Bacopa is the bacosides. An effective dose is 150 mg of bacosides daily.
5) Creatine
Creatine is an important source of energy for the cells. However, it is rarely mentioned that some of the most important receivers of this energy are the neurons.
At this stage, it has been established that the intake of creatine as a nutritional supplement has exclusive benefits for people who suffer from creatine deficiency in the brain.
This may be due to genetic disorders, as well as to the absence of meat in their diet, which is the major dietary source of creatine. Vegetarians belong to the risk group. The serious shortage of creatine leads to significant cognitive abnormalities.
Creatine has potential benefits to support brain activity in healthy people. Besides the positive effect on memory, creatine is known as a strong anti-fatigue means, especially in the absence of a sound sleep.
Its benefits can be critical for periods of extreme exhaustion.
Dosage:
- The recommended intake of creatine is in the form of creatine monohydrate, as the daily dosage ranges between 2 and 5 grams per day.
Alcohol And Drugs, Stress, Fatigue, Lack of Sleep, Depression
They are all explicit saboteurs of a good memory. Our cells need a balanced diet and plenty of time to rest to function properly. This applies in full force to the brain cells as well.
If selected food properly undoubtedly has a beneficial effect on the brain and mental activity. According to analyses of US researchers, about 90% of the people with mental disorders significantly improve their lifestyle after changing their daily menus.
The exact mechanism of the effect of food on the brain is still not known. Each food product has different ingredients and components. It is difficult to say exactly which one and how it is most active in the brain cells.
The combination of different substances is most likely to be of importance for the final effect. The menu of an adult dealing with head work must contain 75-90 grams of fats a day - animal and vegetable.
Fruits and vegetables containing vitamin C are beneficial for active brain activity. 50 grams of dark chocolate a day can also slow the aging of the brain.
Which Foods Feed Best Our Brain
- Proteins: stimulate the brain cells; play a role in the speed and quality of the nerve impulses;
- Carbohydrates: give glucose that is required for all brain processes;
- Fatty acids: support the memory functions of the memory;
- Microelements: these are antioxidants that restore cellular damages and that activate the brain.
Foods that act as antioxidants are particularly useful for the functioning of the brain. They neutralize the free radicals - the culprits of damage, malfunctioning, and cell aging. Some of the best food antioxidants are olive oil, soybeans, eggs, spinach, broccoli, cranberries, cabbage, beets, and citrus fruits.
Carbohydrates help one remember more easily and also support the active work of the brain, but it's better for a person to get them mainly from rice, black bread, potatoes. Iron is a microelement with essential importance for the proper brain function.
TOP 10 "Smart" Foods
- Grapes: Grapes increase the level of dopamine, which improves memory and stimulates the brain.
- Raisins: Raisins have compounds of the element boron, which activates and tones the memory.
- Spinach: Spinach – the lutein therein protects the brain cells.
- Blueberries: Blueberries – they activate the cells of the gray matter in the brain in parts of the brain responsible for remembering.
- Soy Milk: Soy milk contains phytoestrogens that improve memory. Soy improves the memory and speeds up the learning process. However, I am not a fan of any soy containing food.
- Oily Fish: Oily fish is a rich source of omega-3 fatty acids and iodine: they are involved in the memory processes.
- Blackcurrant: Blackcurrant is rich in vitamin C.
- Pumpkin Seeds: Pumpkin seeds contain a large dose of zinc that accelerates the brain.
- Liver: Liver is a rich source of vitamins of group B. These vitamins improve memory and relax the nervous tension.
- Cheese: Cheese - contains large amounts of the l-tryptophan amino acid, which recently scientists have linked to the formation and expression of leadership and managerial qualities in a person.
Which is your favorite brain-boosting acetylcholine supplement or stack? Share what works for you!
Last Updated on September 12, 2024 by Kaira




